DIGITAL MARKET RESEARCH
“Research is what to do when we don’t know what to do”
the phrase “research is what to do when we don’t know what to do” highlights the crucial role that research plays in directing our strategies and actions. Research acts as a compass in the always changing world of marketing, guiding us through ambiguity and allowing us to make wise judgements. Research delivers the data-driven insights required to chart the proper course, whether it’s for uncovering undiscovered prospects, comprehending our target audience, or evaluating market dynamics. By revealing user preferences and potential problems, it plays a crucial part in product development. Additionally, it guides our selection of budgetary allocation, risk-reduction tactics, and marketing channels, ensuring that resources are focused where they can have the biggest impact. Research also promotes a culture of adaptation, allowing us to stay ahead of the curve in a setting that is changing quickly by keeping abreast of new trends and technology.
1. What is digital market research ?
The systematic method of gathering, analysing, and interpreting data from digital or online environments to learn more about consumer behaviour, market trends, and competitive dynamics is known as “digital market research.” Information from websites, social media platforms, search engines, and e-commerce platforms is gathered through utilising digital tools and technology. Understanding client preferences, evaluating market prospects, and guiding strategic decision-making in the digital space are all accomplished through the use of quantitative and qualitative approaches in digital market research.
How digitalization has transformed market research ?
Market research has undergone a seismic change as a result of digitalization, which has also revolutionised how organisations collect and use data. The ease of access to and speed of data collecting has undergone one of the most significant changes. In the past, time-consuming and frequently geographically constrained traditional market research techniques like surveys and focus groups were used. With the advent of digitalization, data can be quickly gathered from a variety of sources around the world using online surveys, social media monitoring, and site analytics. Researchers are able to record and analyse customer opinions and trends as they emerge thanks to this real-time access to a massive database of data, which enables businesses to make more rapid and data-driven decisions.
Digitalization has also substantially improved the depth and granularity of insights. It was difficult to discern specific client behaviours and preferences in traditional market research because aggregated data was frequently presented. Digital tools and technology, however, enable surveillance and analysis that is extremely personalised. Businesses that use advanced analytics can segment their audiences more precisely and learn more about the demands and journey of each individual client. This level of specificity makes it possible to develop marketing campaigns and product offerings that are highly targeted, enhancing client happiness and promoting growth. In essence, market research has become more rapid due to digitalization, but it has also improved in terms of quality and granularity, enabling firms to adjust to the digital age and survive.
2. Research Objectives
Digital market research is essential to this project since it acts as our compass in the always changing online environment. We manage this unpredictable landscape by having well defined objectives, which help us find insightful information and business prospects. We’ll review the main goals of digital market research in this conversation, emphasising how they help us understand customer behaviour, anticipate market trends, outperform rivals, and make data-driven decisions that lead to success in the digital sphere.

These goals act as the constellation’s compass points for digital market research. Organisations confront enormous potential as well as major problems in the quickly changing digital landscape. These research goals serve as lighthouses, illuminating the way ahead and assisting organisations in making sense of the digital world.
Organisations can understand customer behaviour, adjust to market developments, and outperform rivals by upholding these aims. They may hone their digital marketing techniques, developing campaigns that connect with their target market and produce measurable outcomes. Digital market research also enables businesses to improve user experience, develop novel products, and make defensible judgements based on factual data.
3. Market Research types
There are many distinct types and approaches of market research, each of which aims to collect particular data to suit particular corporate objectives.
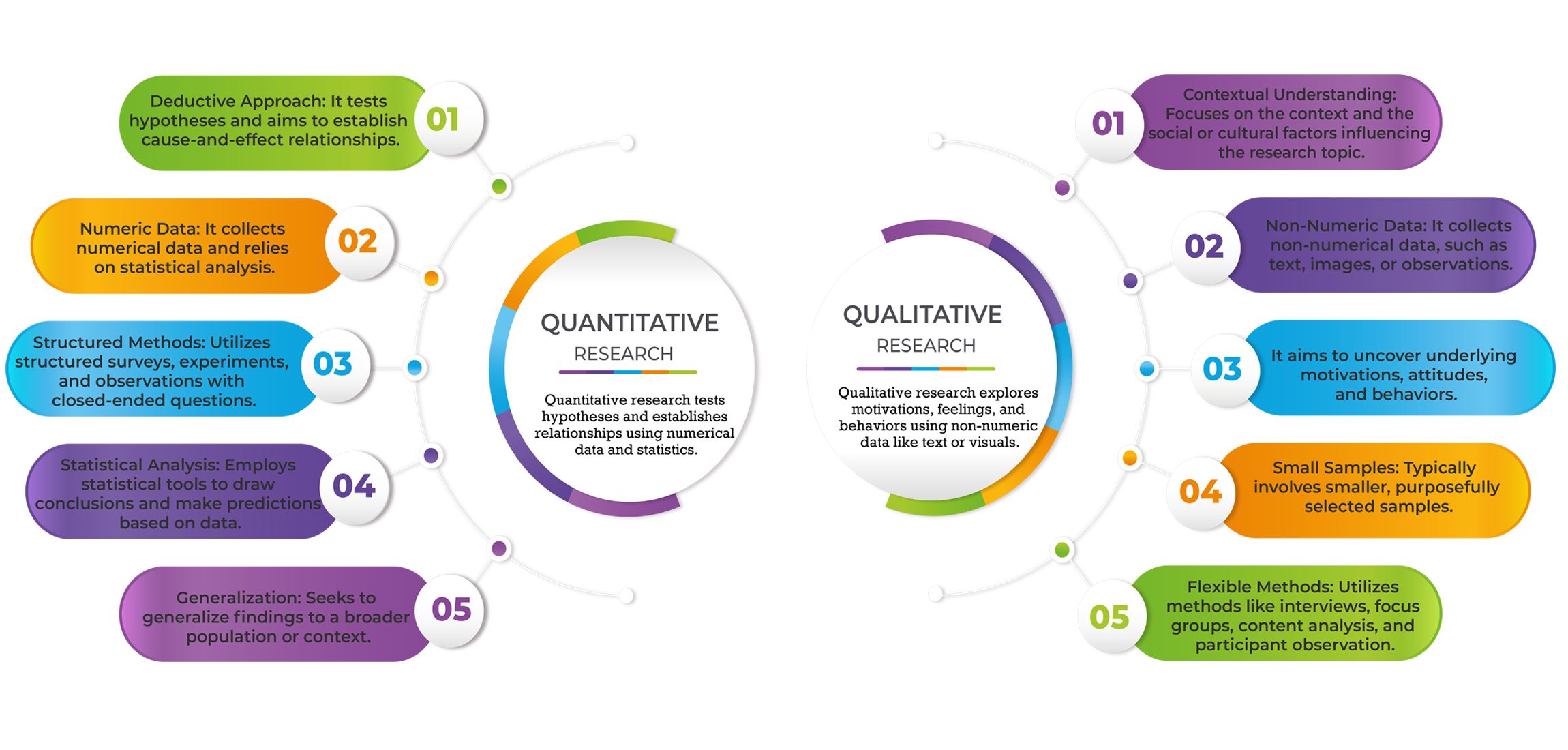
Qualitative Research:
Focus groups, in-depth, open-ended interviews, and observations are all part of qualitative research. It seeks to glean insightful, nuanced information on customer attitudes, drives, and perceptions.
Descriptive Research:
This kind of study tries to describe a market’s features, including its size, demography, and purchasing patterns. It offers a fundamental comprehension of the market landscape.
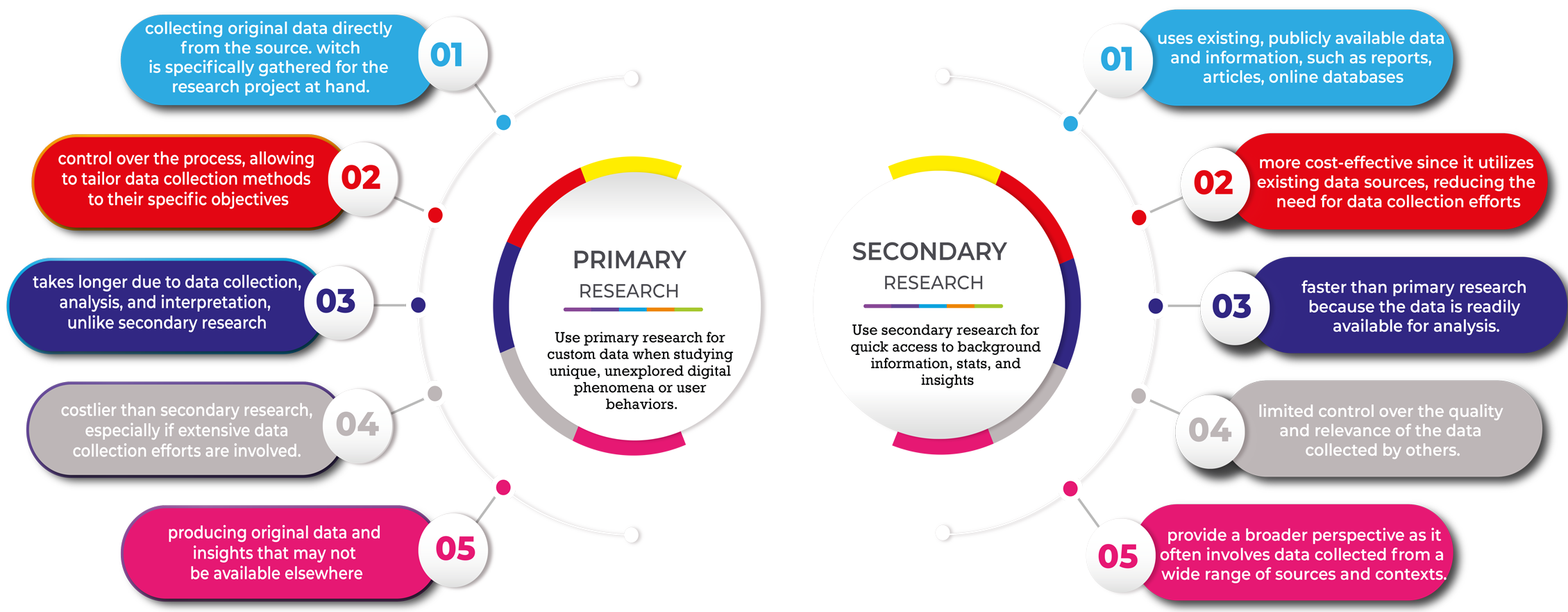
Secondary Research:
The utilisation of pre-existing data and information from publicly accessible sources, including industry reports, scholarly research, and official publications, is known as secondary research. It is an affordable method of learning new things without doing fresh research.
Quantitative Research:
Quantitative research involves structured data collection methods, such as surveys and experiments, to gather numerical data for statistical analysis. It provides quantifiable insights into market trends and consumer behavior.
Exploratory Research:
Exploratory research is utilised by businesses when they want to learn more about an issue or phenomenon. It aids in the development of more precise research questions and hypotheses.
Primary Research:
Primary research involves collecting original data directly from sources, such as surveys, interviews, and observations. It is customized to address specific research questions and is tailored to the unique needs of a study.
Qualitative vs. Quantitative Research
Primary vs. Secondary Research
4. Digital Research Methods
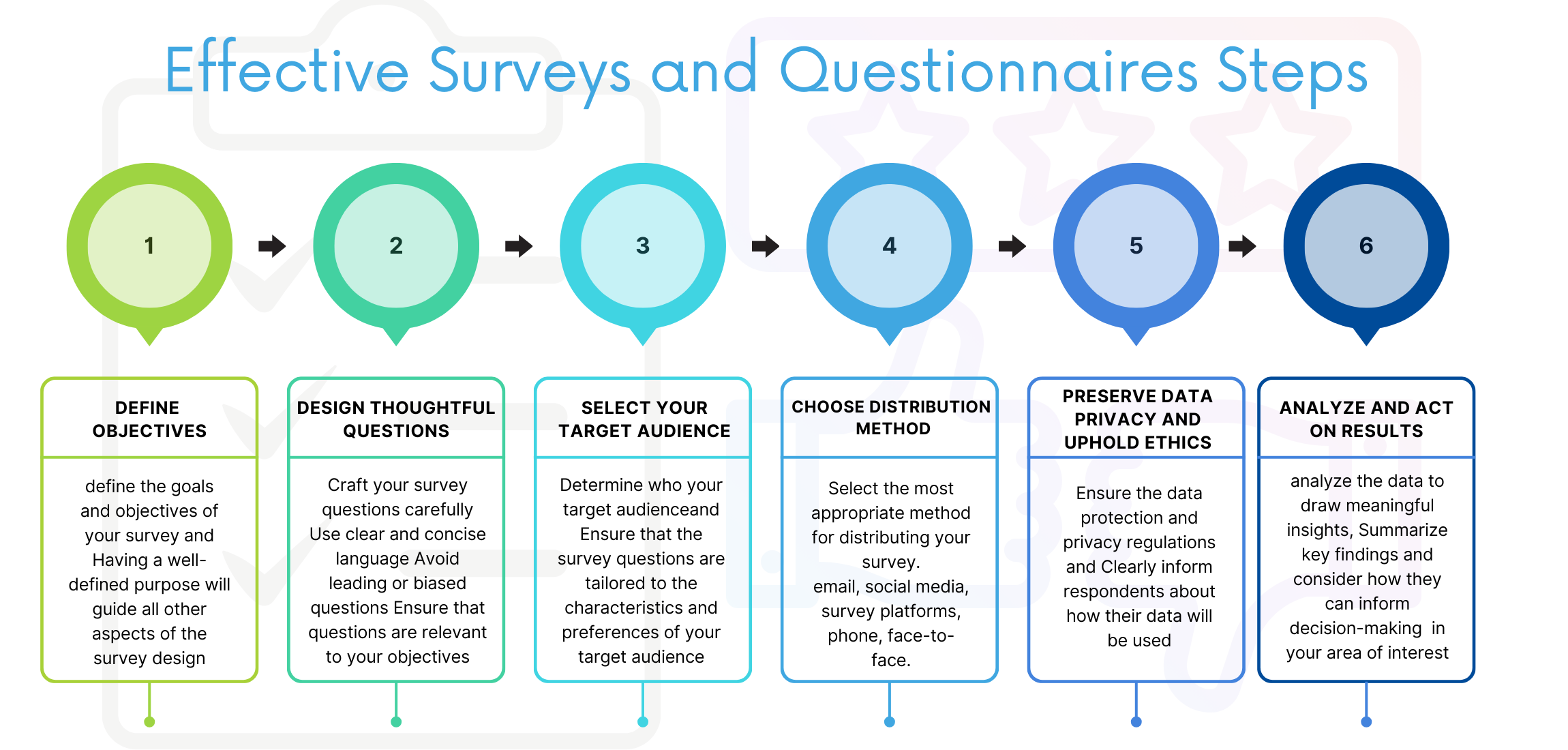
A. Surveys and Questionnaires
Surveys
A survey is a research technique used to gather information from a pre-selected set of respondents in order to learn more and obtain new perspectives on a variety of interesting topics. They are frequently used to gather demographic information, viewpoints, and sentiments on a given subject.
Questionnaires
A questionnaire is a type of research tool used to gather data from respondents and consists of a series of questions or other prompts. Data on a variety of subjects, including demographics, opinions, attitudes, behaviours, and knowledge, can be gathered via questionnaires.
Although “survey” and “questionnaire” are frequently used synonymously, there is a small distinction between the two. The entire procedure of gathering, combining, and analysing data from a group of respondents is referred to as a survey. The questions used to get the data are part of a questionnaire. In other terms, a survey includes a questionnaire.
B. Social Media Monitoring
The technique of actively observing and analysing social media channels to obtain data, insights, and trends about particular subjects, keywords, businesses, or people is known as social media monitoring, sometimes known as social media listening or social media tracking. This method is frequently employed for a number of objectives, such as reputation management, market research, competition analysis, and comprehending client sentiment.
Software platforms known as “social listening tools” enable people and organisations to actively monitor and analyse social media channels for mentions of their brands, products, or particular keywords. These tools are essential for market research, managing online reputations, and social media marketing.
C. Web Analytics TOOLS
Google Analytics
With the help of Google Analytics, which is a feature-rich web analytics solution, website owners and marketers may track and examine many facets of website traffic and user behaviour. It provides information on the demographics of the audience, user behaviour trends, and conversion monitoring. Real-time data, e-commerce monitoring, event tracking, and the ability to design unique reports and dashboards are all additional features of the platform. By assisting users in understanding how visitors engage with their online assets and helping them make data-driven decisions to improve user experiences and meet business objectives, Google Analytics plays a significant part in optimising websites and marketing efforts.
Heatmaps and Session Recordings
Insights into user behaviour and preferences on websites and digital platforms can be gained using effective market research techniques like heatmaps and session recordings. By monitoring mouse movements and clicks, heatmaps visually depict the webpage elements that attract the most and least attention. This information allows organisations to place important content, buttons, and calls to action in the most effective locations. Real-time user interactions are captured in session recordings, which enable researchers to study how users move around a website, where they get stuck, and where they give up. These techniques help in finding usability problems, boosting user experience, and raising conversion rates.
5. Market Segmentation and Targeting
Targeting and market segmentation are two crucial marketing ideas. The technique of splitting a market into groups of consumers with comparable needs and wants is known as market segmentation. Selecting one or more segments to concentrate your marketing efforts on is the process of targeting.
Demographics (age, gender, income, education, and occupation), psychographics (interests, values, and lifestyle), and behavioural characteristics (buy history, website visits, and social media participation) are just a few of the techniques used to segment the market. Following market segmentation, the decision of which categories to target will rely on the specific marketing goals, the resources at hand, and the distinctive value offer of the company. This tactical choice makes sure that marketing initiatives are precisely tailored to appeal to the most pertinent and receptive client groups, thus fostering success in a cutthroat industry.
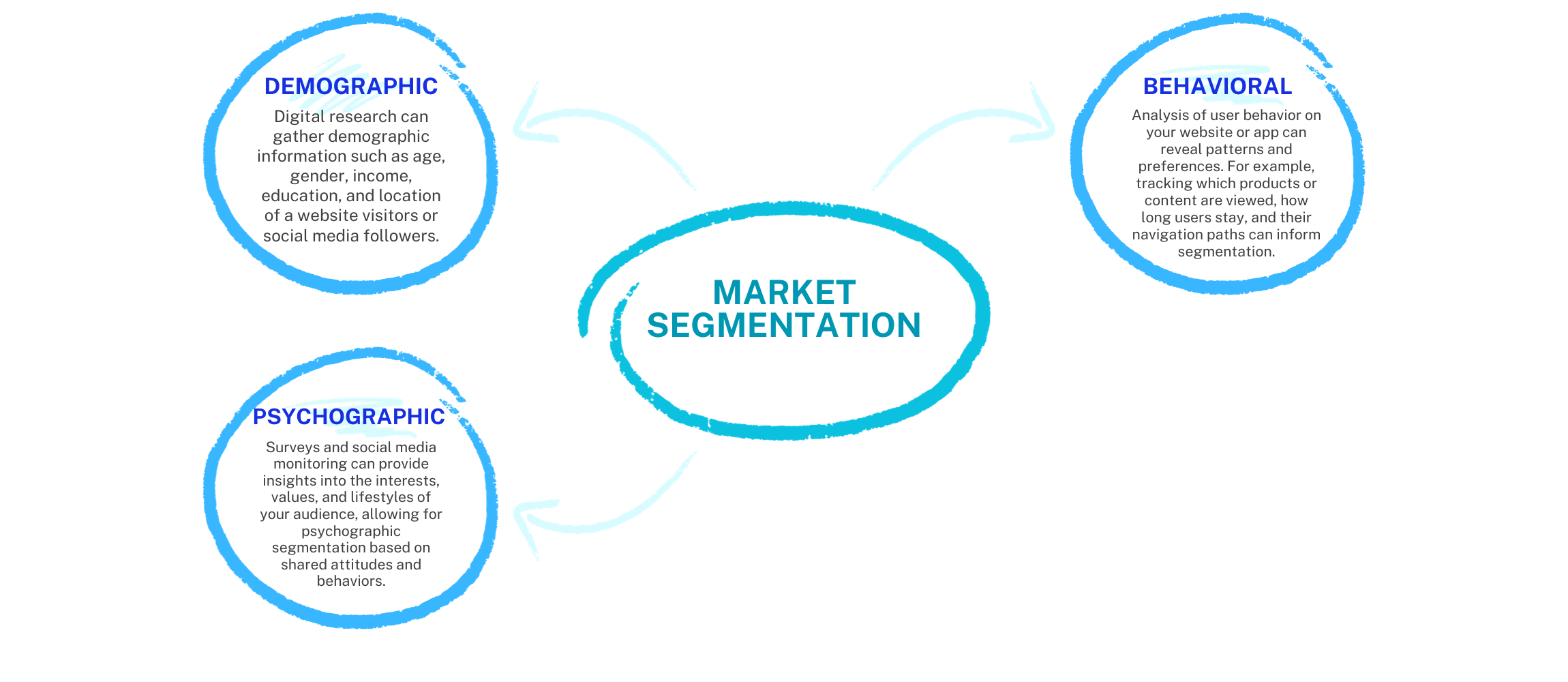
Digital research is essential for compiling demographic data about website visitors and social media followers, including their age, gender, income, education, and geography. Based on these qualities, this data is the foundation for establishing separate market groups, allowing firms to better target their content, marketing plans, and product development. It supports personalization, content, and targeted advertising techniques, ultimately boosting user experience and return on investment. In order to remain relevant in the rapidly growing digital landscape, it is crucial to handle this data with the utmost privacy and conformity to laws.
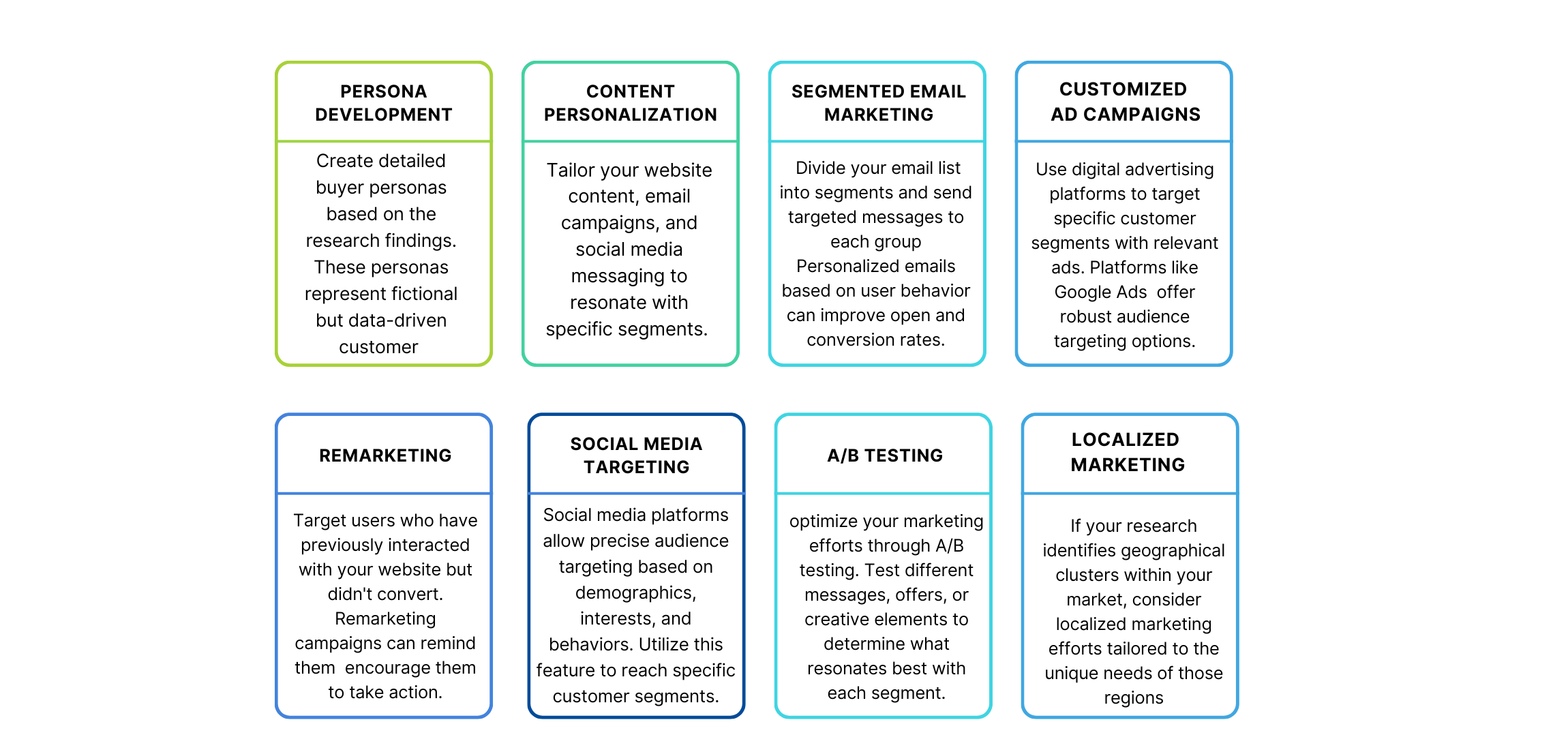
STRATEGIES FOR TARGETING SPECIFIC CUSTOMERS
6. Competitor Analysis
A competitor analysis, also known as a competitive analysis or competition analysis, is the process of looking at companies that are similar to yours in your industry in order to learn more about their products, branding, sales, and marketing strategies. If you’re a business owner, marketer, start-up founder, or product developer, it’s critical to understand your competition in business analysis.
A competition study has a number of advantages, such as helping you comprehend industry standards so you can meet and exceed them, finding underserved niches and differentiating goods and services, additionally satisfying consumer needs and resolving issues more effectively than rivals, differentiating your brand, and Making a statement with your advertising and tracking your development.
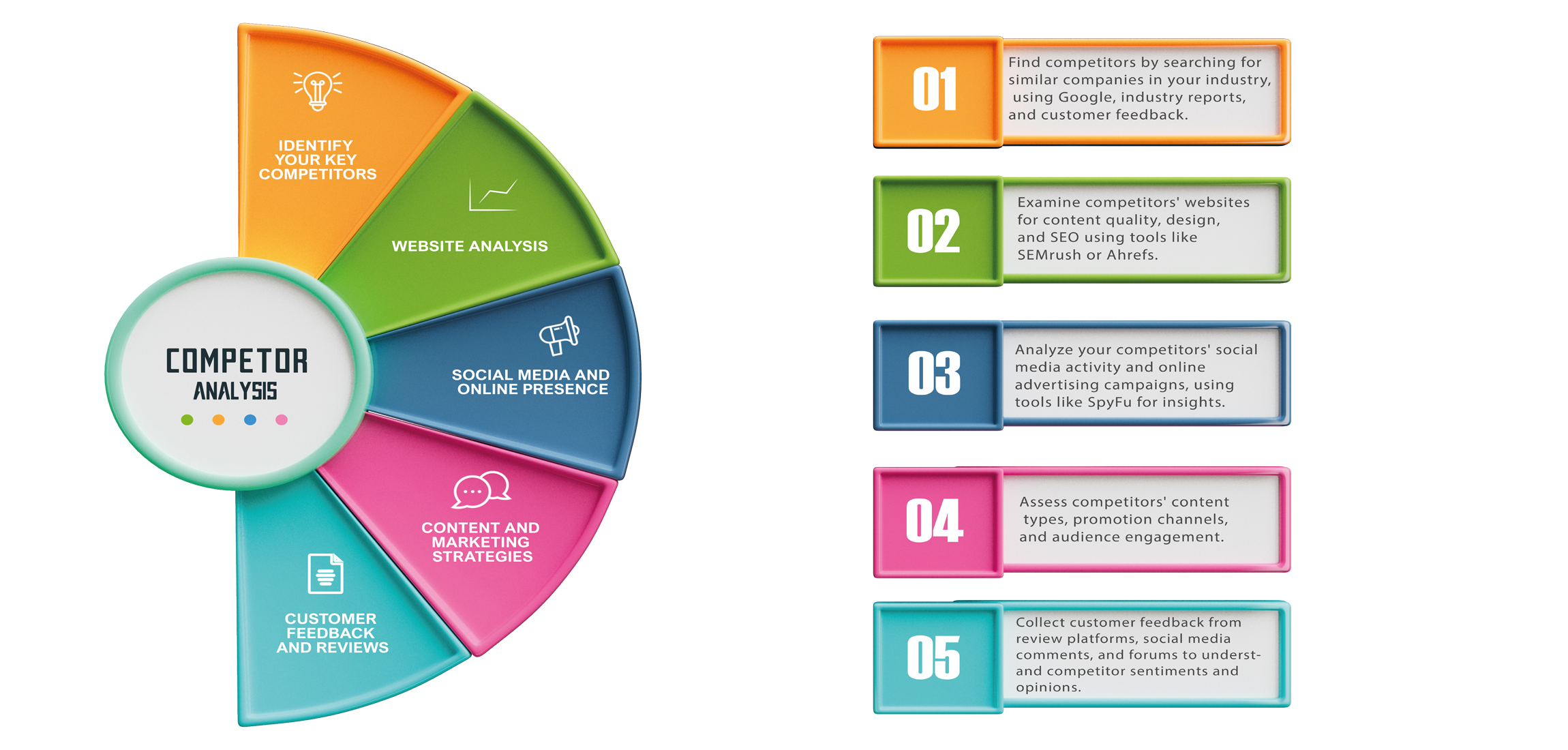
Developing a strong company plan requires identifying and evaluating competitors. Start by “Identifying Your Competitors” to compile a list of direct and indirect competitors in your industry before beginning a thorough competition analysis. After that, evaluate their online presence, user experience, and content quality by doing a “Website Analysis”. Understanding their activity, follower engagement, and strategy on different platforms is the main goal of “Social Media Presence” study. “Content Analysis” aids in determining the formats and subjects of popular content. “Backlink Analysis” shows their link-building activities, while “Keyword Research” reveals their SEO strategy. Keep an eye on “Online Advertising” to learn more about their PPC advertisements and initiatives. To understand their “Email Marketing” strategies, subscribe to their newsletters.Lastly, to obtain a competitive advantage in your sector, use “Benchmarking” to assess how you perform in comparison to rivals across important parameters. Remaining ahead of the curve in the ever changing digital world requires frequent upgrades and improvements.
7. Market research Proces
The systematic process of gathering, analysing, and interpreting data for the purpose of learning more about markets, consumers, and rivals is known as market research. Informing business decisions, seeing opportunities, and reducing risks all depend on it. The market research process entails setting goals, developing research techniques, gathering data, analysing results, and coming up with wise recommendations. Through better understanding of consumer wants, market trends, and competitive environments, organisations can better plan their strategies and achieve better business results. Effective market research is crucial for remaining competitive and responsive to shifting market conditions in this dynamic and always changing company environment.

8. Case Studies and Practical Examples
Coca-Cola’s “Share a Coke” Campaign:
Coca-Cola has a global marketing initiative called “Share a Coke.” It debrands the classic Coca-Cola logo by swapping out “Coca-Cola” on one side of a bottle with the words “Share a Coke with” and a name. The campaign tries to get consumers to go looking for a bottle with their name on it and then share it with their friends. It employs a list of 250 of each market country’s most popular names (in certain cases, generic nicknames and titles are also utilised). Australia hosted the campaign’s launch in 2011.
The Share a Coke campaign was then launched in more than 80 nations. According to estimates from the advertising firm Ogilvy in Australia, the campaign raised Coke’s market share by 4% and young people’ consumption by 7%. At the Cannes Creative Effectiveness Lion Awards, the campaign won numerous prizes.


Airbnb’s Data-Driven Strategy
With the use of statistics, Airbnb makes important judgements. Through randomised controlled studies, the business verifies potential product ideas. The data science team at Airbnb makes predictions about the likelihood of a match using historical data. Airbnb has created a tool to assist hosts in setting prices to maximise the possibility of reservations based on information from millions of stays. In order to comprehend the trip ideation process and the additional services that customers want, Airbnb could apply machine learning.
An online marketplace for both short- and long-term homestays and experiences is run by the American corporation Airbnb, which has its headquarters in San Francisco. The business functions as a broker and takes a commission from each reservation. The corporation has been heavily criticised by citizens of tourist destinations while simultaneously being praised for revolutionising the tourism industry.
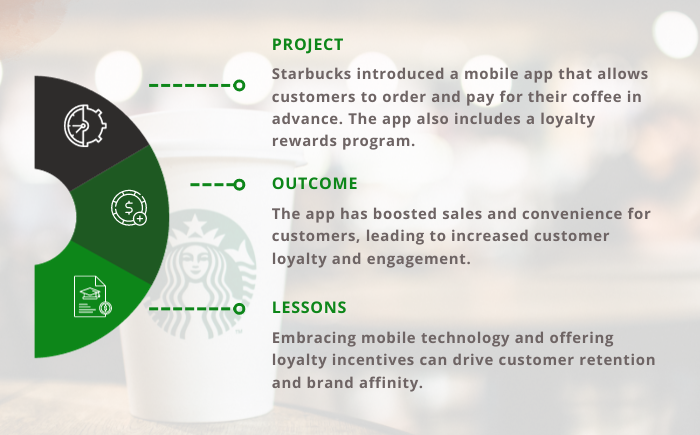
Starbucks’ Mobile Ordering and Rewards App
Starbucks’ Mobile Ordering and Rewards App is a perfect example of how a successful digital strategy can completely change an industry. Through this app, customers can quickly place orders and make purchases at Starbucks using their smartphones, revolutionising the experience. This function reduced physical lines and improved consumer convenience, making it especially helpful on busy mornings. Additionally, Starbucks Rewards, a crucial component of the programme, encouraged repeat business by awarding stars for each transaction that could be exchanged for free drinks and food. The success of Starbucks can be attributed in part to the loyalty programme, which not only encouraged repeat business but also encouraged customers to make mobile payments in order to accrue incentives.
Another important element in the success of the app was its emphasis on customization. The ordering experience was made more efficient and fun for users by using client data from prior orders to deliver personalised recommendations. The software also included store finding and guidance services, enabling users to track their orders in real-time, and easily linked with mobile payment options. As a result, there was a noticeable increase in consumer engagement and loyalty, less crowding in-store, and useful information on client preferences. In the fiercely competitive coffee sector, Starbucks’ Mobile Ordering and Rewards App is a shining illustration of how ease, personalisation, and loyalty rewards can propel digital success while providing insightful data for continuous business strategy advancements.